Are Cell Membranes Freely Permeable to Water
In this figure Selective permeability of cell membrane. The membrane forms a completely closed bag and it is found by trial and error that adding the cells to a solution of a particular concentration of sucrose.

Lipid Bilayer Permeability Physiologyweb
The size and electric features of molecules determine their ability to cross cell membranes.

. Volume increases on the side with more solutes. The diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane in response to a concentration gradient is known as osmosis. This characteristic is why cell membranes are selectively permeable.
The membrane forms a completely closed bag and it is found by trial and error that adding the cells to a solution of a particular concentration of sucrose results in neither swelling nor shrinking of the cells. In order to allow water to move in and out cells have special proteins that act as a doorway. As the cell wall is permeable to various molecules nutrients like water and oxygen and excretion substances it is said to be freely permeable as in most plants and it allows the entry and exit.
The membrane is selectively permeable because substances do not cross it indiscriminately. The cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane meaning that it allows the passage of water and some select solutes. Water molecules diffuse across membrane toward solution with more solutes 4.
Many large molecules do not move across the membrane freely. The movement of carbon dioxide molecules across the cell membrane is described as osmosis. Selective Permeability Cell membranes only allow some molecules through.
Osmosis refers exclusively to the diffusion of water molecules across the cell membrane. Small molecules without electric charges eg gases and oil-soluble molecules can cross membranes almost freely. If a membrane is permeable to water though not to a solute water will equalize its own concentration by diffusing to the side of lower water concentration and thus the side of higher solute concentration.
More solute molecules lower concentration of water molecules 2. Cells must also allow water to enter but water facilitates a free flow of protons and cells cannot allow protons to flow freely. The plasma membrane of most cells is freely permeable to water.
Ions charged particles do not move across the membrane freely. This quality allows a cell to control what enters and exits it. What is semi-permeable membrane give examples.
Only small non-polar molecules are able to freely diffuse across the cell membrane. Instead the chloroplast electron transport system is located in the thylakoid membrane and protons are pumped across this membrane from the stroma to the thylakoid lumen. Cell membranes are selectively permeable.
The small but highly polar water molecule is still able to diffuse across artificial membranes rapidly with a permeability coefficient of 34 10 3 cms. Lipid membranes are semi-permeable also called selectively permeable. Cells normally occupy an environment with a particular concentration of solutes.
Small and simple molecules like water H2O can pass through the cell membrane easily as it is partially permeable. In a separate experiment the freezing point of that particular sucrose. The human red-blood-cell membrane is freely permeable to water but not at all to sucrose.
Cell wall is freely permeable while cell membrane isdifferentially permeable. In this way the plasma membrane is said to be selectively permeable. No cell walls are made of cellulose while cell membrane fromlipo-proteins.
The membrane is called semipermeable meaning that some things can pass through without assistance while other things cannot. The outer membrane of the chloroplast envelope like that of mitochondria contains porins and is therefore freely permeable to small molecules. An example of a biological semi-permeable membrane is the lipid bilayer on which is based on the plasma membrane that surrounds all biological cells.
What type of substances pass through the cell membrane most easily. The human red-blood-cell membrane is freely permeable to water but not at all to sucrose. The role of integral membrane proteins in.
In order for a molecule or charged molecule to enter a cell it often requires energy input. The cell wall allows various nutrients like water and carbon dioxide to step directly into the cell. Although water small nonelectrolytes and gases are freely permeable through most biological membranes apical membranes of certain barrier epithelia exhibit extremely low permeabilities to these substances.
As the cell wall is permeable to various molecules nutrients like water and oxygen and excretion substances it is said to be freely permeable as in most plants and it allows the entry and exit of the molecules. What substances are permeable to the cell membrane. They are not impermeable not letting anything pass nor are they freely permeable letting everything can pass.
In comparison even slightly larger polar metabolites such as urea and glycerol have lower permeability across artificial membranes approximately 10 6 cms 35 39. Cell membranes only allow some molecules through. Membrane must be freely permeable to water selectively permeable to solutes 3.
They are not impermeable not letting anything pass nor are they freely permeable letting everything can pass. There is a cell membrane also present inside the cell wall in the plant cells. The smallest molecules such as water carbon dioxide and oxygen can diffuse freely across cell membranes.
Water is a charged molecule so it cannot get through the lipid part of the bilayer. Permeability is lower for uncharged molecules such as water and glycerol. This quality allows a cell to control what enters and exits it.
Water moves across the membrane freely. The challenge is that histidine is about 700000 times the size of a proton. No degree of leakiness in a membrane will succeed in keeping protons out while allowing histidine and water in.
Why is the cell membrane cell selectively permeable and freely permeable.
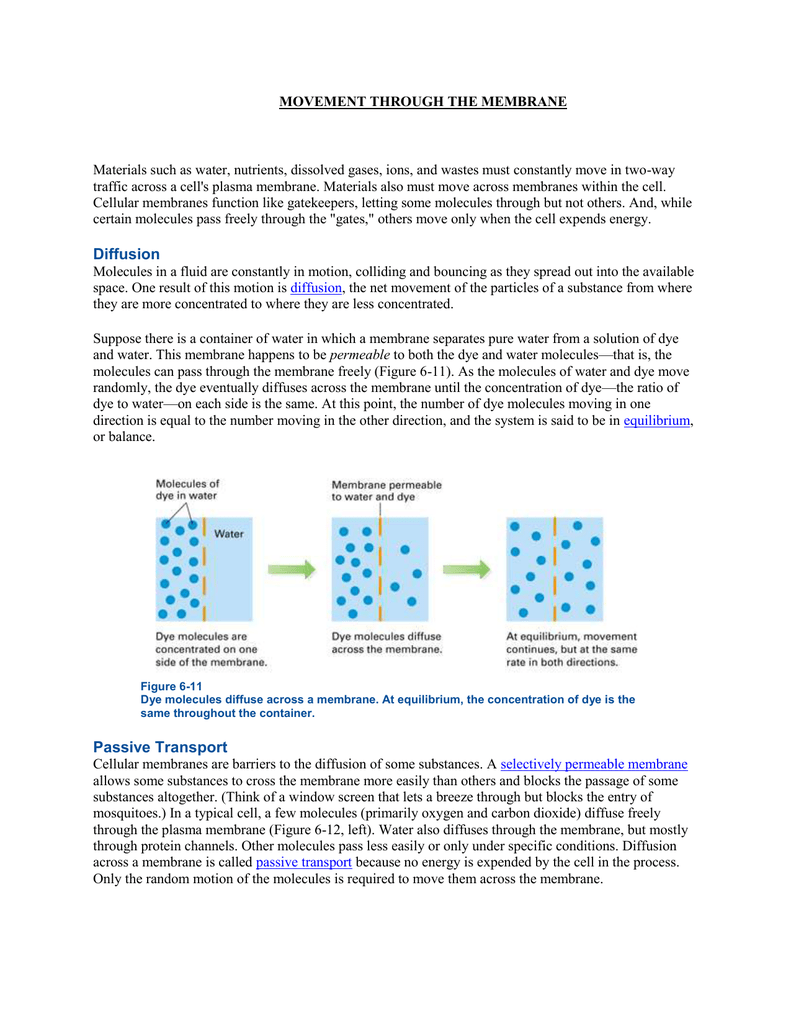
Movement Through The Membrane Materials Such As Water

Passive Transport Boundless Biology

Semipermeable Membrane Definition Examples Biology Dictionary

Selective Permeability Definition And Function Biology Dictionary
Types Of Cell Membrane Transport Structures Course Hero

Why Is The Cell Membrane Permeable To Lipid Soluble Molecules Quora

Biological Inspiration And Molecular Design Of Highly Selective And Download Scientific Diagram

Plasma Membrane Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Chapter 7 Transport Across Cellular Membranes In Fundamentals Of Cell Biology On Openalg

Cell Membrane And Transport Cell Membrane Plasma Membrane Is Semi Permeable Or Selectively Permeable Because It Controls What Enters And Exits The Ppt Download
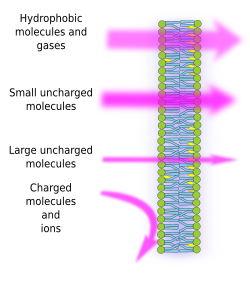
The Cell 3 Cell Membrane Permeability Fluidity Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
What Would Happen If Cell Membranes Suddenly Became Permeable Instead Of Selectively Permeable Could Cells Remain Alive Explain Your Thinking Quora
3 5 Passive Transport Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
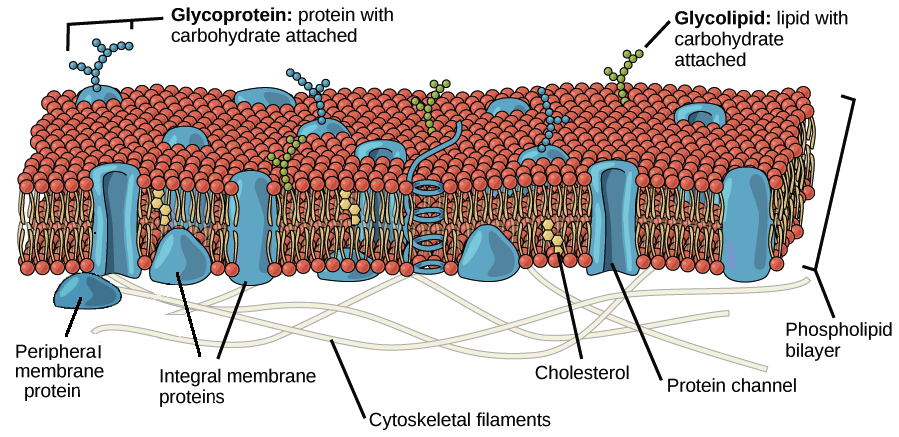
The Cell Membrane Review Article Khan Academy

Selective Permeability Of The Cell Membrane Osmosis

Selective Permeability Definition And Function Biology Dictionary
Selective Permeability Of Dialysis Tubing Lab Explained Schoolworkhelper

Comments
Post a Comment